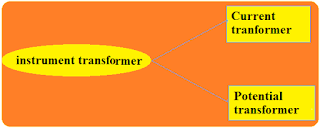
Instrument Transformer.
Purpose using this transformer
Instrument transformers used for measurement and protection purposes in substations.
Parts and working principle of instrument transformer.
- Primary winding
- secondary winding
- Core
The alternating current or voltage generated at the secondary winding is directly proportional to the alternating current or voltage at its primary winding. In simple words, Instrument transformers are the type transformer which reduces the voltage and current from a higher value to a lower value for measurement, protection, and controls purpose.
A Primary winding receives a high amount of current or voltage from the main bus bar and converts it into a suitable value for measurement, Protection, and control purposes.
Instrument transformers have a very low burden value (VA ratings) so this cannot be used for power transmission. This is a major difference between the instrument transformer and the power transformer.
Classification of instrument transformer based on its installation
- If the transformer is installed at the switchyard then it is called 'Outdoor instrument transformer'.
- If the transformer is installed at the switchgear inside the panels then it is called 'Indoor Instrument transformer'.
Can we use an instrument transformer for measuring current and voltage?
Classification of instrument transformer based on its application
Measurement purpose.
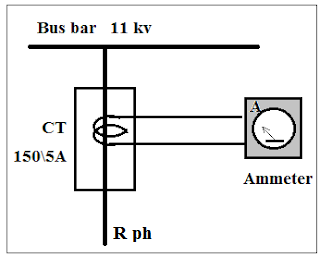
If the secondary winding of the instrument transformer is connected to the measuring devices such as Analog Ammeter, Analog Voltmeter, watt-meter, or Digital meters then this type of transformer is for measurement purposes.
Protection purpose.
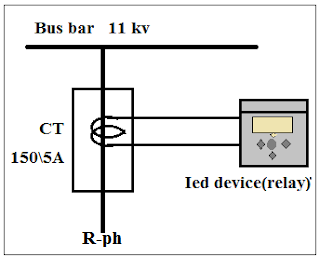
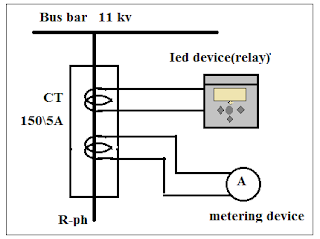
If the secondary winding of the Instrument transformer is connected to the IED devices (Intelligent Electronic Device) such as Numerical relay, Differential relay, etc then this type of instrument transformer is used for protection purposes.
From the above mentioned, we came to know that Current transformers(CT) and Potential Transformers(PT) are called instrument transformers.
- To reduce "current" from a higher rating to a lower rating, we have to use the current transformer (CT). Secondary current is 5 Amp or 1 Amp (r.m.s).
- To reduce "voltage" from a higher rating to a lower rating, we have to use the potential transformer(PT). This is also called 'Voltage transformer'.Secondary voltage is 110 volts (r.m.s).
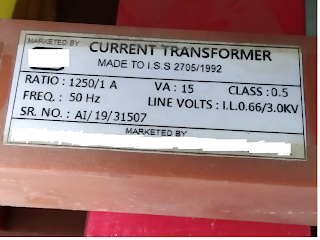
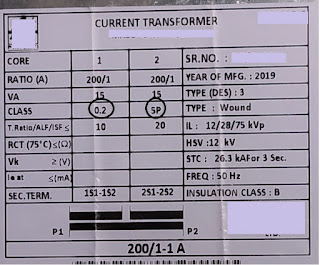
Current Transformer.
The current transformer reduces current for metering purposes in its secondary winding which is proportional to the current in its primary winding. The current transformer is a "step-up transformer" because the number of turns in the secondary winding is more when compared with the primary winding. The current transformer is a series-connected type instrument transformer.
Ns > Np
The current transformer is also called CT. The secondary side of the current transformer(CT) must be shorted while operating because the high voltage is generated at the secondary terminal, high voltage may cause arching or blast in CT.
According to the connection of primary winding, the current transformer is basically classified into.
- Wound-type current transformer.
- Toroidal-type current transformer.
- Bar-type current transformer.
1.Wound-type current transformer.
The primary side of the wound-type current transformer is directly connected with the live conductor.
2.Toroidal-type current transformer.
The toroidal transformer doesn't have a primary side. It has a window-type hole through which the conductor will pass.
3.Bar-type current transformer.
Bar type current transformers consist of a bar on the current transformer. The Primary winding is surrounded on the bar and ends of the bar connected to the conductor.
- Measuring core current transformer.
- Protective core current transformer.
How to identify "Measuring core current transformer"?
How to identify "Protective core current transformer"?
Double-core current transformer.
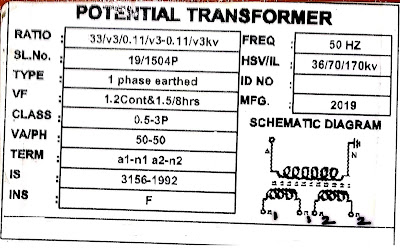
The potential transformer reduces the voltage on its secondary winding which is proportional to the voltage on its primary winding. A Potential transformer or voltage transformer is the 'step down transformer' its secondary winding is less when compared with the primary winding.
Ns<Np
A primary side of the potential transformer is connected from phase to phase or phase to earth i.e., we can use it for three-phase and for a single phase. Voltage transformers may be either single-phase or three-phase.
There are two types of constructions:
- Electromagnetic Potential transformer in which the primary side and secondary side are wound as a normal transformer.
- Capacitor potential transformer in which the primary side is taken through a series capacitor group i.e., Primary voltage flow through a series capacitor. The voltage across one of the series capacitor is taken to the auxiliary voltage transformer. The secondary side of the voltage transformer is taken for measurement or protection purposes.
How to find measuring voltage transformer?
As same as the current transformer, the voltage transformer also has 'Class'. If the class is 0.1 to 1.0 then it is for measurement purposes. The ratio error is due to the impedance of the voltage transformer winding.
How to find the protection voltage transformer?
Nameplate for measuring and protection voltage transformer.
Double core Potential transformer
From the above-mentioned name-plate potential transformer have two cores that are represented as 'Term' (a1-n1 and a2-n2). One core 'Class' represented as 0.5 and another one is represented as 3P.






Nice blog thanks for sharing such an informative blog ,the way you express your views are so easy to understand . if you want to buy Special Purpose Transformer in India, Visit Transformer Manufacturers in pune, One of the best Transformer Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteNice Blog!
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this informative blog.If you are looking for the best Transformer Manufacturers in India or all over India then
please contact us.
Transformer Manufacturers in India
Transformer Manufacturers in Pune
Transformer Manufacturers in Mumbai
Transformer Manufacturers
Transformer
Control Transformer
Step Down Transformer
Isolation Transformer
Nice Blog!
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this informative blog. Trutech Products is growing Transformer Manufacturers in India, we serve outstanding services to our clients.
Transformer Manufacturers In Mumbai
Transformer Manufacturers In India
Thanks for sharing this blog .It's Very Usefull for me.
ReplyDeleteTrutech Product is the leading Transformer Manufacturers in Pune at the best cost visit us for:
Transformer Manufacturers In Mumbai
Transformer Manufacturers In India
Thank you so much for this information. If you are looking for Transformers Manufactureres in Pune, Visit Trutech Products, One of the best Transformer Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for this information. If you are looking for Transformers Manufactureres in Pune, Visit Trutech Products, One of the best Transformer Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteThank You For This Nice Blog, It Helps Me Alot.
ReplyDeleteIf ou want to knowfurther about, Transformer Manufacturers in India Visit Trutech Products, One of the best .Transformers Manufacturers in Pune
Thank You For This Nice Blog, It Helps Me Alot.
ReplyDeleteIf ou want to knowfurther about, Transformer Manufacturers in India Visit Trutech Products, One of the best .Transformers Manufacturers in Pune
Thank You For This Nice Blog, It Helps Me Alot.
ReplyDeleteIf ou want to knowfurther about, Transformer Manufacturers in India Visit Trutech Products, One of the best .Transformers Manufacturers in Pune
Thank you for giving this wonderful blog.
ReplyDeleteTrutech Products is one of the best Transformer Manufacturers in Mumbai. Contact us or visit our website if you are looking for best Transformer Manufacturers in Pune.
Transformer Manufacturers In India
Thanks for sharing this article as it enlighten us about types of Transformers. As a [Distribution Transformer Manufacturers][1], we understands about the products and their uses as per the need. So, Our Team are able to manufacture customized transformers as per the requirement of client that met to national and international standards.
ReplyDelete[1]: https://www.macroplasttransformers.com/distribution-&-power-transformers.html
Thank you Current Transformers Outdoor
ReplyDeleteThank you Current Transformers Outdoor
ReplyDeleteThank you for your blog Potential Transformer Manufacturers
ReplyDeleteThank you or your blog Transformer Manufacturers
ReplyDeleteThank you for your blog Distribution Transformer Manufacturers
ReplyDeleteOne of India's Top Distribution Transformer Manufacturer is Macroplast Transformers was founded in 1979. We are the top manufacturer and exporter of oil-filled, dry type, amorphous core, special purpose, and three-phase distribution and power transformers as well as single and three-phase transformers.
ReplyDeleteServokon is one of the Best Power Transformer Manufacturers in India. We provide the top quality with the help of our expert team of engineers and always keep a check on their technical and quality standards which has helped us to provide the best services.
ReplyDeleteExcellent Blog. Thanks for the great information.
ReplyDeleteIf you are searching for Current Transformer Manufacturers, Ereva is the perfect option for you.